- ISC2 Community
- :
- Discussions
- :
- Tech Talk
- :
- Wanted one answer on domain 5
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Wanted one answer on domain 5
Hi I have looked at one question from Shon Harris book. Books says that answer C is correct. I looked at many sites before asking this question.
My understanding says that
if threshold is too low (sensitivity high) then False positive will be more i,e. nonintrusive activity are considered attacks .
If threshold is high( sensitivity low), false negative will be more i.e. attacks will not be identified.
Kindly support with explanation which is correct option and why others are not correct?
B. If the threshold is set too low, nonintrusive activities are considered attacks (false negatives). If the threshold is set too high, then malicious activities are not identified (false positives).
C. If the threshold is set too high, nonintrusive activities are considered attacks (false positives). If the threshold is set too low, then malicious activities are not identified (false negatives).
D. If the threshold is set too high, nonintrusive activities are considered attacks (false positives). If the threshold is set too high, then malicious activities are not identified (false negatives).
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@savita1974 wrote:My understanding says that
if threshold is too low (sensitivity high) then False positive will be more i,e. nonintrusive activity are considered attacks .
If threshold is high( sensitivity low), false negative will be more i.e. attacks will not be identified.
George is responsible for setting and tuning the thresholds for his company’s behavior-based IDS. Which of the following outlines the possibilities of not doing this activity properly?A. If the threshold is set too low, nonintrusive activities are considered attacks (false positives). If the threshold is set too high, then malicious activities are not identified (false negatives).
B. If the threshold is set too low, nonintrusive activities are considered attacks (false negatives). If the threshold is set too high, then malicious activities are not identified (false positives).
C. If the threshold is set too high, nonintrusive activities are considered attacks (false positives). If the threshold is set too low, then malicious activities are not identified (false negatives).
D. If the threshold is set too high, nonintrusive activities are considered attacks (false positives). If the threshold is set too high, then malicious activities are not identified (false negatives).
One way to attack questions is to look at what you are looking at, in this case comparing:
A. too low (false positive), too high (false negative)
B. too low (false negative), too high (false positive)
C. too high (false positive), too low (false negative)
D. too high (false positive), too high(false negative)
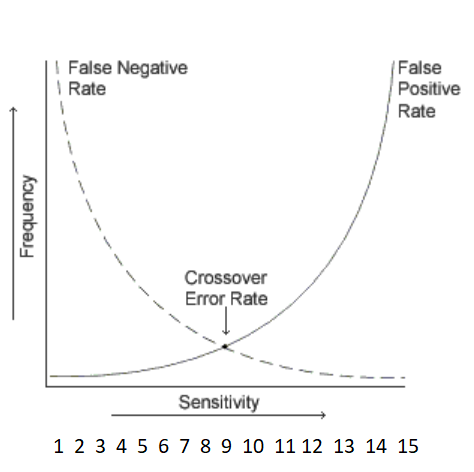
Now look at what are we being asked to look at? You are being asked to examine what is the problem with false responses, i.e. What is worse when tuning an IDS? The worst things would be 1) Missing an actual attack caused by a false negative. 2) Spending a lot of time chasing fake attacks caused by false positives. You have probably seen the chart below in your studies. As you increase sensitivity the false negative rate decreases and the false positive rate increases. In this case your ideal threshold would be around 9, where you get your crossover error rate where the false negatives and false positives (hopefully) equal out. Knowing this knocks out answers A & D as being incorrect. B can be eliminated as the definitions are not correct for the scenario provided. A non-attack is not considered a false negative (a fake indicator that an attack is not happening), it is a false positive (a fake indicator that an attack is happening). Since nonintrusive activities are not considered attacks (false positives) and NOT false negatives, Answer B is eliminated and the second half of B is wrong also.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
As I told all of my seminars, I refuse to answer ANY question that begins, "Shon Harris says ..."
(Shon did a great service in bringing together a lot of disparate material in a very readable form. But she developed a huge tendency to "explain" things that she actually didn't, in any way, understand ...)
............
Other posts: https://community.isc2.org/t5/forums/recentpostspage/user-id/1324864413
This message may or may not be governed by the terms of
http://www.noticebored.com/html/cisspforumfaq.html#Friday or
https://blogs.securiteam.com/index.php/archives/1468
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
Am in the process of studying for CISSP certification (exam May 14th) - I came across this question in a practice test and I dont seem to be able to logically wrap my head around the answer as given in the book.
////////////// start
From the All-In-One study guide (Harris, Maymi) Chapter 5 test p855 question 21:
George is responsible for setting and tuning the thresholds of his company's behaviour-based IDS. Which of the following outlines the possibilities of not doing this activity properly?
A) If the threshold is set too low, non intrusive activities are considered attacks (false positives). If the threshold is set too high, malicious activities are not identified (false negatives).
B) If the threshold is set too low, non intrusive activities are considered attacks (false negatives). If the threshold is set too high, malicious activities are not identified (false positives).
C) If the threshold is set too high, non intrusive activities are considered attacks (false positives). If the threshold is set too low, malicious activities are not identified (false negatives).
D) If the threshold is set too high, non intrusive activities are considered attacks (false positives). If the threshold is set too high, malicious activities are not identified (false negatives).
Answer: C
I answered A. If you set a threshold of 3 then 3 failed logins will be considered an attack - the lower the bound the more general the trigger (this could just be someone not typing their password in properly). If the bound is set high then if a login fails after 10 attempts its more likely an attack.
//////////end
What am I missing in my understanding? The answer in the book just repeats the actual question and does not provide an explanation:
“ If the threshold is set too high, non intrusive activities are considers attacks (false positives). If the threshold is set too low, malicious activities are not identified (false negatives).”
How are malicious activities not identified if the threshold is set low? It seem counter-intuitive to me, more gets captured on a low threshold than on a high threshold.
Cheers
Ray
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
So after typing that out for 20 minutes I think I figured it out. If the threshold is high to achieve success it may be out of reach for non-intrusive activities to achieve success. Whereas if the threshold is low for a success case more success are granted than should be. So the threshold is for success not failure - I think I had this backwards in my understanding.
Not sure why I was not able to see that previously - possibly I am studying too much......
cheers
Ray
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
I just posted this same question and was redirected here.
I want to point out the following from the All-in-one book p832:
"Determining the proper thresholds for statistically significant deviations is really the key for the successful use of a behavioral-based IDS. If the threshold is set to low. non-intrusive activities are considered attacks (false positives). If the threshold is set too high, some malicious activities wont be identified. (false negatives)"
This is A in the answer not C by the books own definition as far as I can tell.
Chers
Ray